Features and Benefits
Advanced Imaging Technologies
Speckle reduction technology
Improves contrast resolution while maintaining detail resolution
Phase-inversion harmonic imaging
Reduces noise and clutter for optimum image quality
Spatial compounding
Multiple lines-of-sight improves contrast resolution
Multi-beam technology
High frame-rate in all modes including color and Doppler
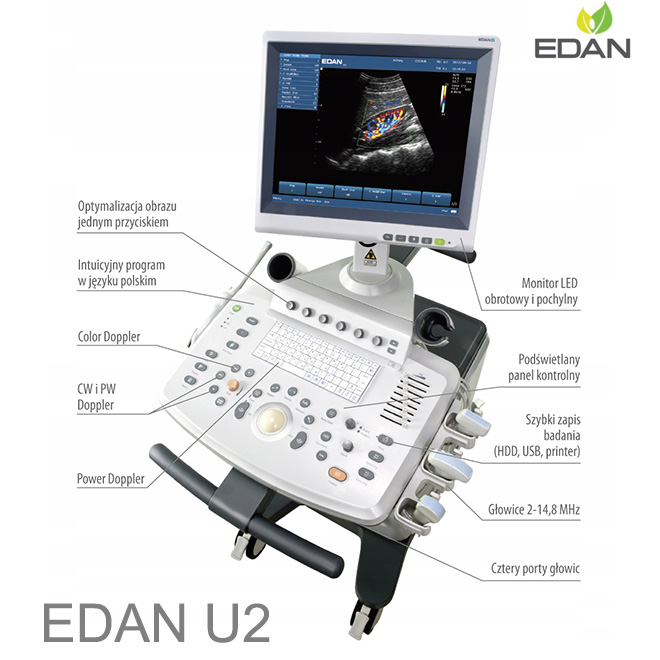
User-friendly Workflow
Intuitive control panel reduces learning curve
Smart PreSet - quickly adjust multiple setting to suit your patient type and imaging preferences
Multi-frequency Transducer Technology
Multiple 2-D, harmonic and color frequencies increases transducer utility
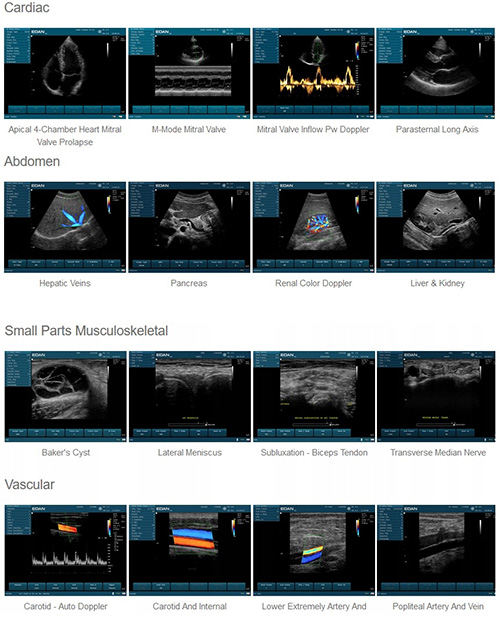
Supported Applications
Abdomen, Obstetrics, Gynecology, Endovaginal, Small Parts, Muculoskeletal, Vascular, Urology, Cardiology, Pediatrics
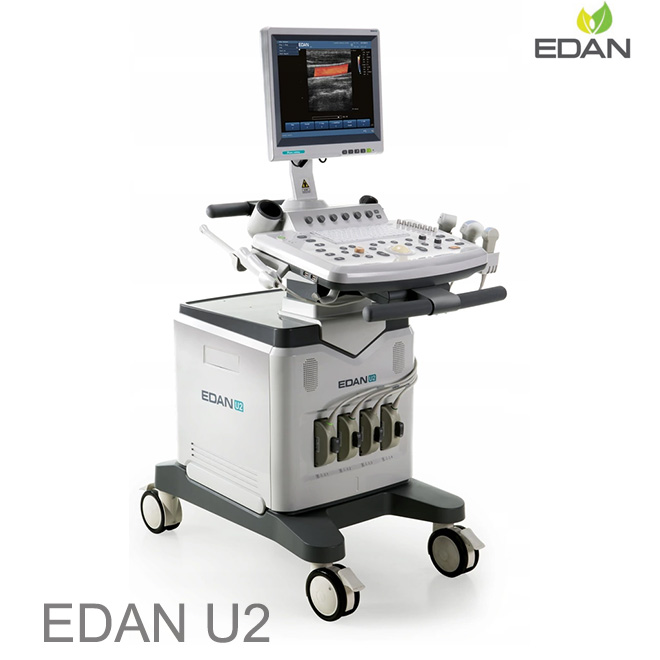
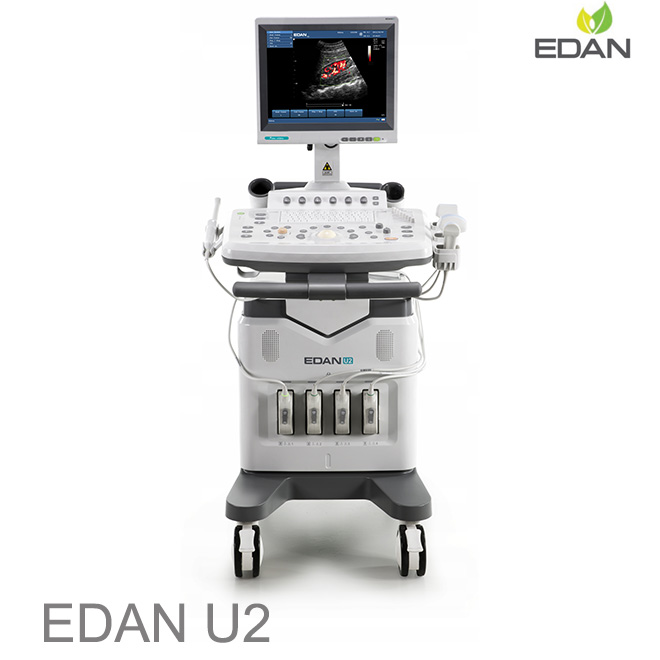
Compact, Mobile Cart Design, Exceptionally quick boot time
Built-in lithium battery
15" High resolution LCD monitor
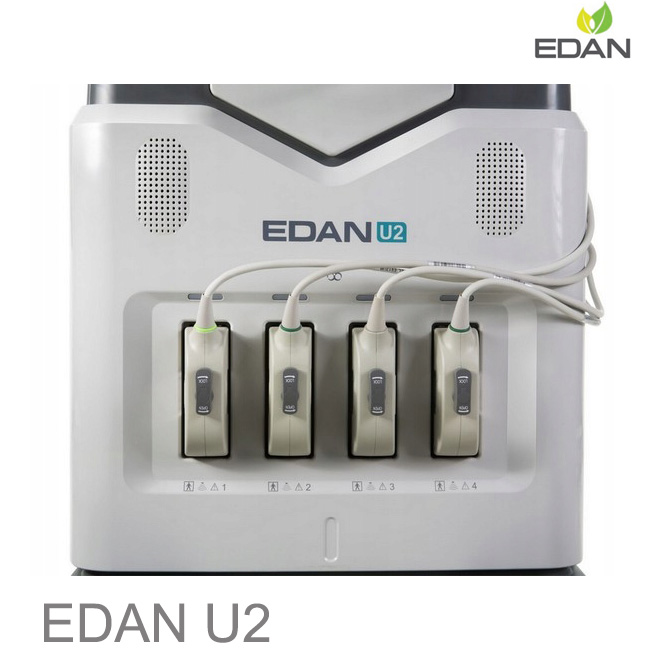
Multiple peripheral ports
Speckle Reduction Technology
Speckle reduction imaging uses real-time image processing to improve visualization of anatomy and pathology by reducing the speckle noise. Edan's speckle noise reduction imaging technology uses an advanced multi-scale anisotropic filtering algorithm. This imaging technology is excellent at separating the noise regions from the diagnostic image allowing complex filtering to be performed differently on noise versus true anatomic information thus producing an enhanced image.
Phase Inversion Harmonic Imaging
Harmonic signals are produced as ultrasound waves propagate through the body. Because these signals are produced in the body, they are not influenced by artifact inducing fat near the skin surface. Consequently, an image formed using only the harmonic signal will have less clutter and can be more diagnostic. With phase-inversion harmonics, pairs of ultrasound pulses with opposite phases are transmitted. When the signals received from inverted pulses are added together, the fundamental components are cancelled and only the harmonic signal remains. This creates an image that is pure harmonic with reduction in clutter artifact that degrades the image.
Spatial Compounding
Spatial Compounding combines several different component images to display an image with improved quality. In addition to the image formed by transmitting ultrasonic waves directly away from the transducer, images are formed with waves that have been electronically steered at an angle away from the transducer. Different degrees of steering can be used to produce multiple, different images.
The speckle in these component images will be different because of the electronic steering, but macroscopic variation – like the brightness variation caused by a liver lesion – will be shared between the component images. By combining the images, the speckle noise is reduced while the image contrast is enhanced.
Multi-beam Technology
Ultrasound systems use beams that are focused electronically to produce high spatial resolution. Signals from the transducer are delayed and added together in the system to produce a focused ultrasound beam. The same signals can be added together with different delays to produce multiple beams. When this is done, the spatial resolution can be improved without reducing the frame rate or the frame rate can be improved without reducing the resolution. As shown below, with dual beamformation the same receive beams are formed with half the transmit beams, thus doubling the frame rate.
Convex array C352UB
Applications:
OB/GYN, Abdomen, Pediatrics, Urology
Frequencies:
2.5/ 3.5/ 4.5/ H5.0/ H5.4 MHz
Linear array L742UB
Applications:
Small Parts, Vascular, Musculoskeletal, Superficial
Frequencies:
8/ 9.5/ 11.0/ H13.0/ H13.4 MHz
Micro-convex array C6152UB
Applications:
OB/GYN, Abdomen, Pediatrics, Urology
Frequencies:
5.5/ 6.5/ 7.5/ H9.0/ H9.4 MHz
Linear array L1042UB
Applications:
Small Parts, Vascular, Musculoskeletal, Superficial
Frequencies:
8.0/ 9.5/ 11.0/ H13.0/ H13.4 MHz,
Micro-convex array C612UB
Applications:
OB/GYN, Abdomen, Pediatrics, Urology
Frequencies:
5.5/ 6.5/ 7.5/ H9.0/ H9.4 MHz
Linear array L552UB
Applications:
Small Parts, Vascular, Musculoskeletal, Superficial, Pediatrics
Frequencies:
4.5/ 5.5/ 6.5/ H5.6/ H6.0 MHz
Micro-convex array C422UB
Applications:
Abdomen, Cardiology
Frequencies:
3.0/ 4.0/ 5.0/ H5.0/ H5.4 MHz
Endovaginal E612UB
Applications:
Obstetrics, Gynecology
Frequencies:
5.5/ 6.5/ 7.5/ H9.0/ H9.4 MHz




 Price is 8-20% Lower Than Other
Price is 8-20% Lower Than Other













![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20150505/201505050942035656.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20150820/201508201430246682.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20160226/201602261629209261.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20220318/202203181130316800.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20170928/201709281055391381.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20170927/201709271820337067.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20170510/201705101845366149.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20170928/20170928114415198.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20211223/202112231557188415.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20150507/201505071028043371.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20211222/202112221706187921.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20160331/201603311420026640.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20190123/201901231853173216.jpg.jpg)
![{pr0int $v['title']/}](https://medicalequipment-msl.com/upload/img/20221020/202210201655209109.jpg.jpg)


