What kind of equipment do hospitals use to take pictures? There are three types of hospital radiology examinations: DR (digital radiography), CT (computerized tomography), and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). For the general public, the general term is "film", what is the difference between DR, CT and MRI?
DR examination
DR Imaging
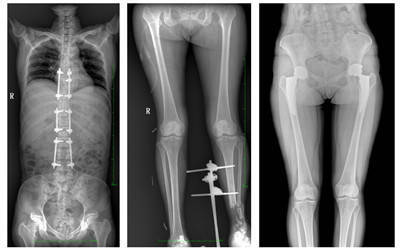
DR examination is also commonly known as X-ray, DR is based on ordinary X-ray, developed into a digital X-ray, commonly understood, is the traditional X-ray advanced version, but the essence is still similar, mainly using the principle of X-ray penetration. Although the examination area and ordinary X-ray film are the same, but the image resolution of DR is significantly higher than X-ray, radiation radiation dose is also reduced very much.
DR examination is commonly used for human chest and bone radiographs, but also other parts of the body, such as the abdomen, teeth, head, etc.. It can be used by a wide range of people to examine all parts of the body, and digital images can be obtained in a few seconds after exposure, which is fast and inexpensive, greatly improving work efficiency and facilitating the diagnosis and treatment of patients with serious clinical conditions and emergencies.
The standing X-ray image is the preferred examination content for determining the biological force line of the weight-bearing bones of the human body, the symmetrical structure smooth line and the scoliosis angle, which is fundamentally different from CT and MRI recumbent imaging in the clinical sense. In the clinical treatment of the spine and lower extremities, which generally requires corrective and joint replacement surgical treatment, standing weight-bearing radiographs are required before and after surgery to analyze the condition, clarify the diagnosis and observe the treatment effect.
PLX8600 large field of view flat panel dynamic DR
The PLX8600 dynamic DR has a large effective field of view of 43cm*86cm, which can image the whole spine and both lower extremities at once.
CT Examination
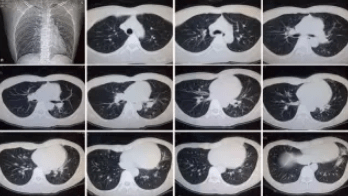
CT Image
The principle of CT examination is that X-rays pass through the body in layers, which is like slicing bread into thin slices, and each slice can be spread out for viewing. When trauma is encountered and bone is suspected, CT can be chosen to look at occult injuries or soft tissue injuries.
CT is applicable to the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis, spine, limbs and bones, etc. Due to its special diagnostic value, it has been widely used in clinical practice, especially in the diagnosis of tumors. However, because CT equipment is more expensive and the cost of examination can be high, there are still some limits to the examination and diagnostic value of certain parts, especially qualitative diagnosis, so CT examination is not considered as a routine diagnostic tool in clinical practice. In addition, CT diagnostic radiation is greater than DR examination, so women who are pregnant or preparing for pregnancy should not undergo CT examination.
MRI examination
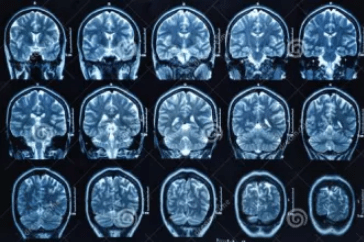
MRI imaging
MRI, also known as magnetic resonance imaging, is a type of tomography, which uses the magnetic resonance phenomenon to obtain electromagnetic signals from the human body and reconstruct information about the body. The examination can obtain cross-sectional, sagittal and coronal images with high spatial resolution, making it the first choice for the detection of the nervous system and the spinal vertebral part of the spine.
MRI is suitable for neurological lesions, cardiovascular system, chest lesions, and soft tissue lesions of the whole body.
Will there be radiation from the film?
There have been patients who have refused to have imaging examinations because of the fear of radiation. In fact, radiation is everywhere, such as radiation from strong ultraviolet rays, radiation from computers, cell phones, etc. These are all daily exposure, and they do not cause harm to the human body.
The common unit of radiation dose is millisievert (mSv), and our country stipulates that each radiologist should not be exposed to more than 20 mSv per year, which is relatively safe in this range. Obviously, the person receiving the examination will not take greater risks than the doctor. And from the medical point of view, generally only when suffering from radiation doses of 100 mSv or more, the probability of the human body developing cancer will increase significantly. We usually come into contact with the means of examination, the radiation dose and this value gap is very large, for example, we often talk about the film, that is, X-ray examination, its radiation dose for the human body is very low, only 0.1 mSv, equivalent to the natural radiation suffered by humans living on earth for 10 days. Such data comparison, do you also feel that the radiation is far less terrible than imagined?
The radiation levels of X-ray examinations and CT examinations are also within the safe range. Therefore, the dose of radiation does not cause harm to the patient's body when undergoing the examination, and there is no need to choose not to do the examination and neglect your health because of the presence of radiation.




 Price is 8-20% Lower Than Other
Price is 8-20% Lower Than Other






